The relationship between SEO and search engines can be described as a “love-hate relationship”. An SEO specialist aims to identify and create the best content for search engines, while search engines aim to find and rank the best content.
Therefore, the basics of SEO cannot be mastered without also mastering the principle by which search engines work. Three terms are important here, crawling, indexing, and ranking.
Definition of SEO
SEO stands for Search Engine Optimization, which refers to the process of enhancing a webpage’s design and structure with the aim of ranking higher on search engines for a specific keyword. The ultimate goal of SEO is to attract high-quality traffic to the website, which can translate into increased profits and boost the site’s authority and brand.
Division of SEO
Although SEO encompasses many activities, it can be divided into three main categories: technical, on-page, and off-page.
- Technical SEO
Technical SEO involves optimizing a website’s infrastructure to improve search engine rankings without altering the content. This includes tasks such as page indexing, speed optimization, and resolving error codes.
- On-site SEO
On-site SEO involves optimizing the content and user experience of a website. It focuses on improving what the visitor sees on the site. Since content is the foundation of all optimization and the primary ranking factor, on-site SEO is crucial and has the most significant impact on a website’s search engine ranking.
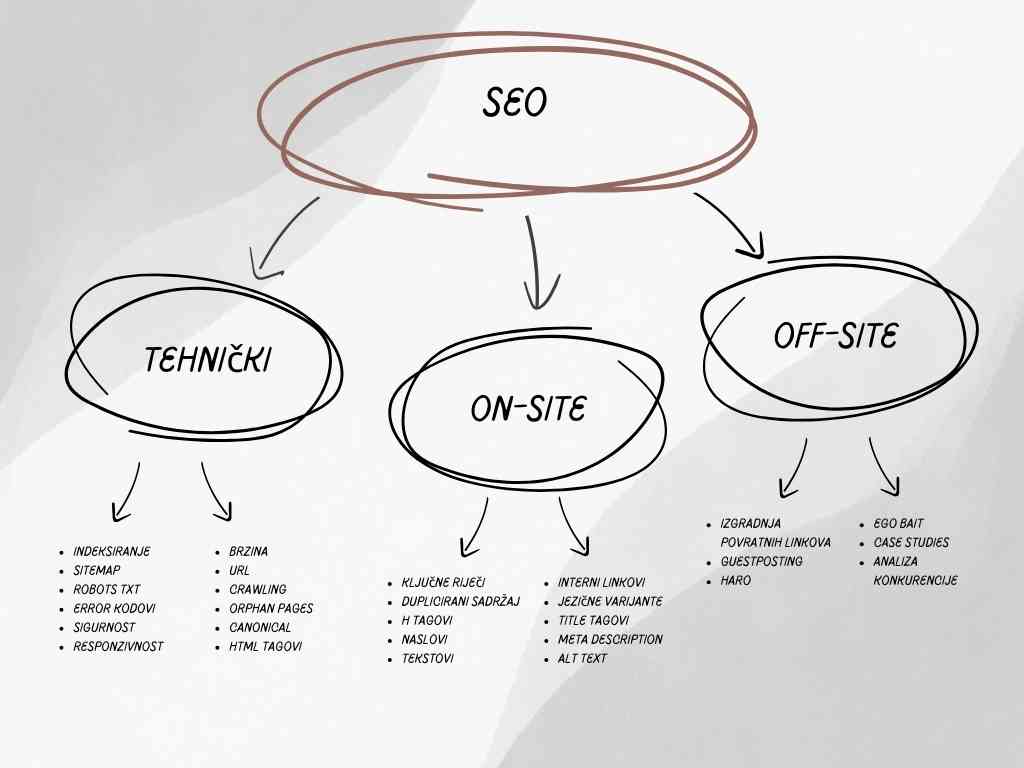
It includes keyword research, content, writing of title tags and meta descriptions, optimization of headers, footers and images, language variants, duplicate content and much more.
- Off-site SEO
Off-site SEO refers to all the optimization activities that are done outside of the website itself, such as acquiring backlinks from external sources. However, it is also the most challenging aspect of optimization as it requires a well-planned strategy and considerable effort to obtain a limited number of high-quality backlinks.
Crawling
Although their algorithm for searching and ranking websites differs, all Internet search engines use the same three principles. The first is crawling.
During the crawling phase, search engines utilize programs that scour the internet and compare its contents with what they already have in their database. They follow links to new pages. If your website lacks links pointing to it, search engines won’t be able to find it on their own. Fortunately, there is a solution to this, which will be further explained in the Google Search Console article.
Indexing
When a web crawler visits a webpage, the first thing it does is to check if the search engine already has that content in its database. If it is in a database, the crawler proceeds to the next page. However, if the content has been updated or changed, the crawler takes note of the changes and updates the database accordingly. This process helps search engines to maintain an up-to-date and comprehensive database of everything available on the Internet.
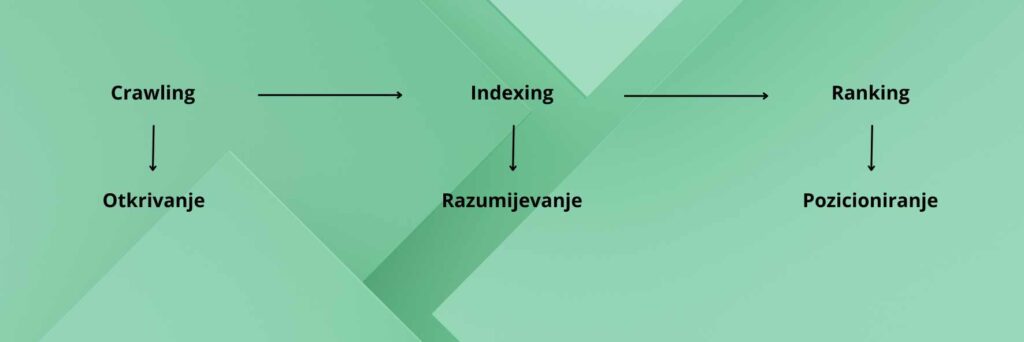
Ranking
All search engines share the same objective – to provide the most useful and relevant answer to the user’s query. Once the crawler has indexed the page, the search engine employs a ranking algorithm to determine the page’s relevance to a particular query and how well it aligns with the user’s intent. Based on this, the search engine displays the page in a specific position in the search results.
Since the ranking algorithms are secret, some search engines do this job better than others.
Sounds simple, but it is not
SEO specialists face a challenging task due to the fact that search engines keep their ranking factors hidden. However, if all the factors were public knowledge, there would be no difference between a skilled and unskilled optimization expert. This could lead to uniform and uninteresting content on the internet.

